Introduction to LLMs
What are Large Language Models?
Language Models are powerful tools that can understand and generate human-like text. Large Language Models (LLMs) take this capability to the next level by utilizing vast amounts of pre-existing text data to learn patterns, context, and linguistic nuances. In this tutorial, we will explore how to create your own LLMs using the Jaseci platform.
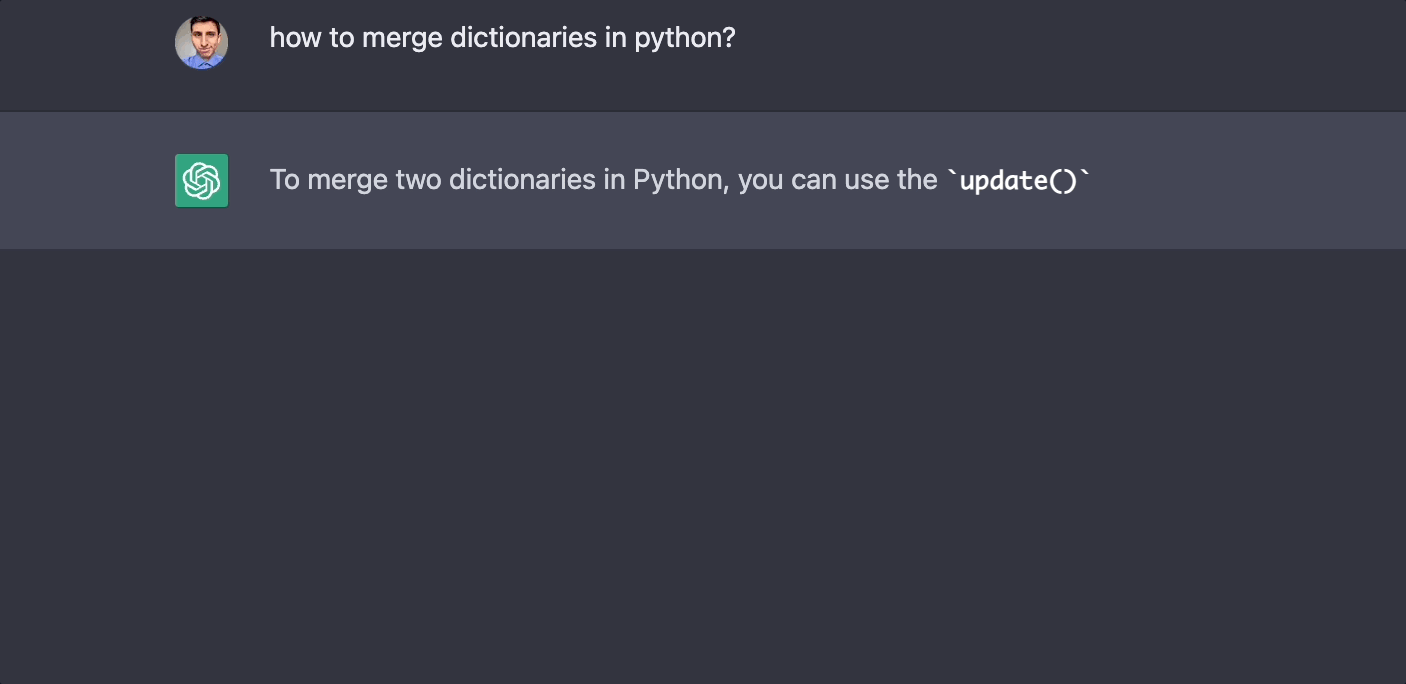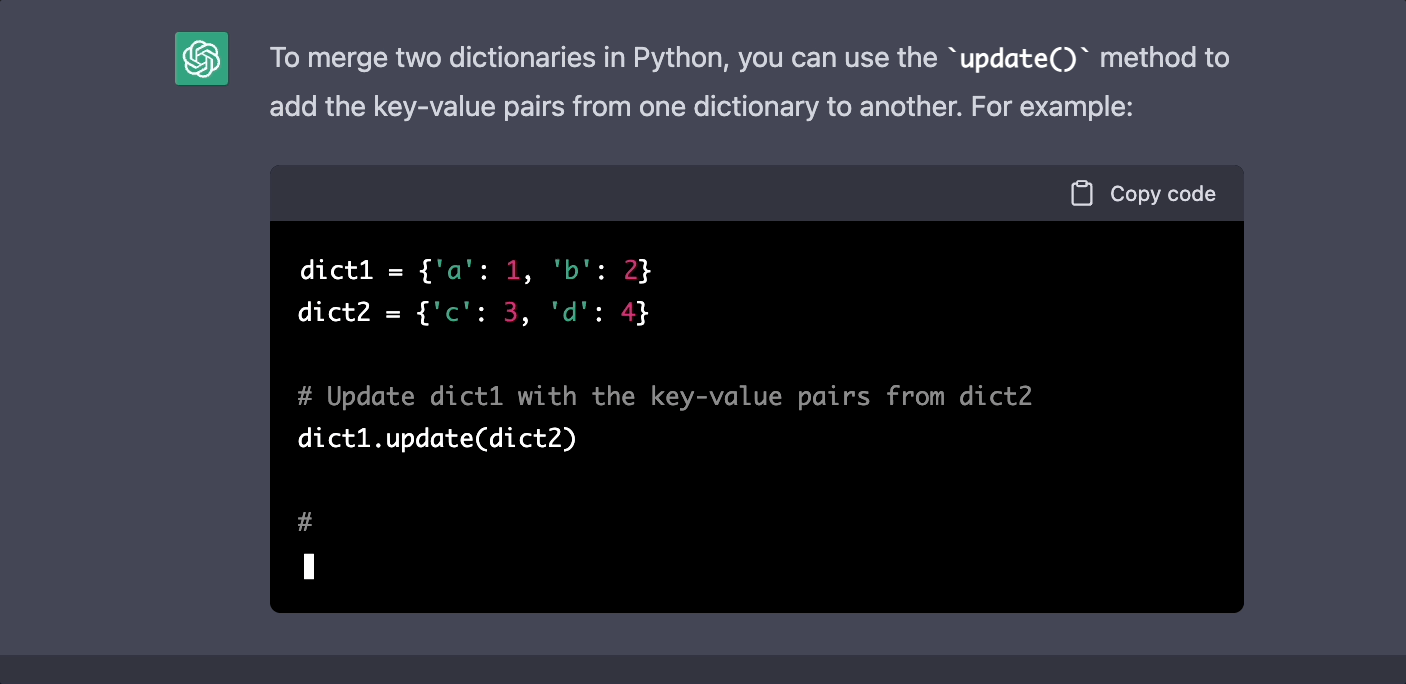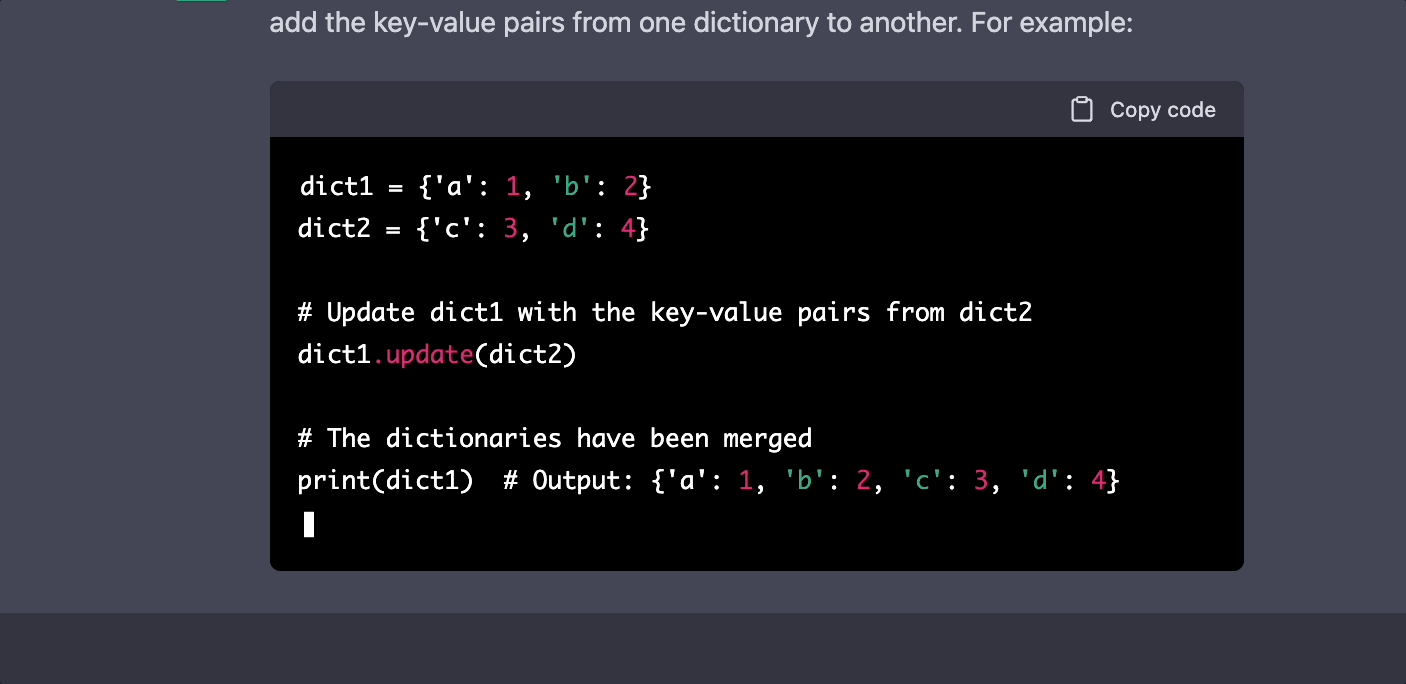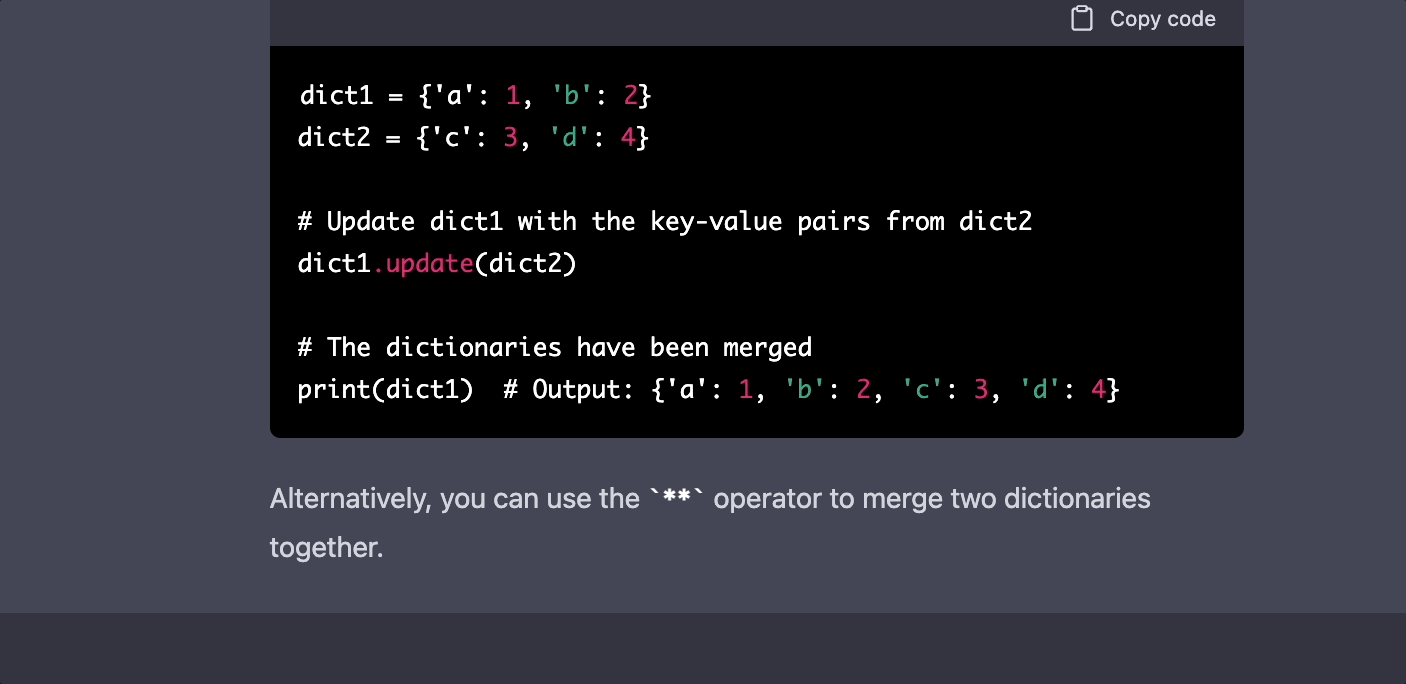
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a neural network-based model that is trained on massive amounts of text data. These models excel at tasks such as text generation, translation, summarization, and question-answering. LLMs are capable of capturing the underlying structure and semantics of language, making them incredibly versatile.
Training a Large Language Model
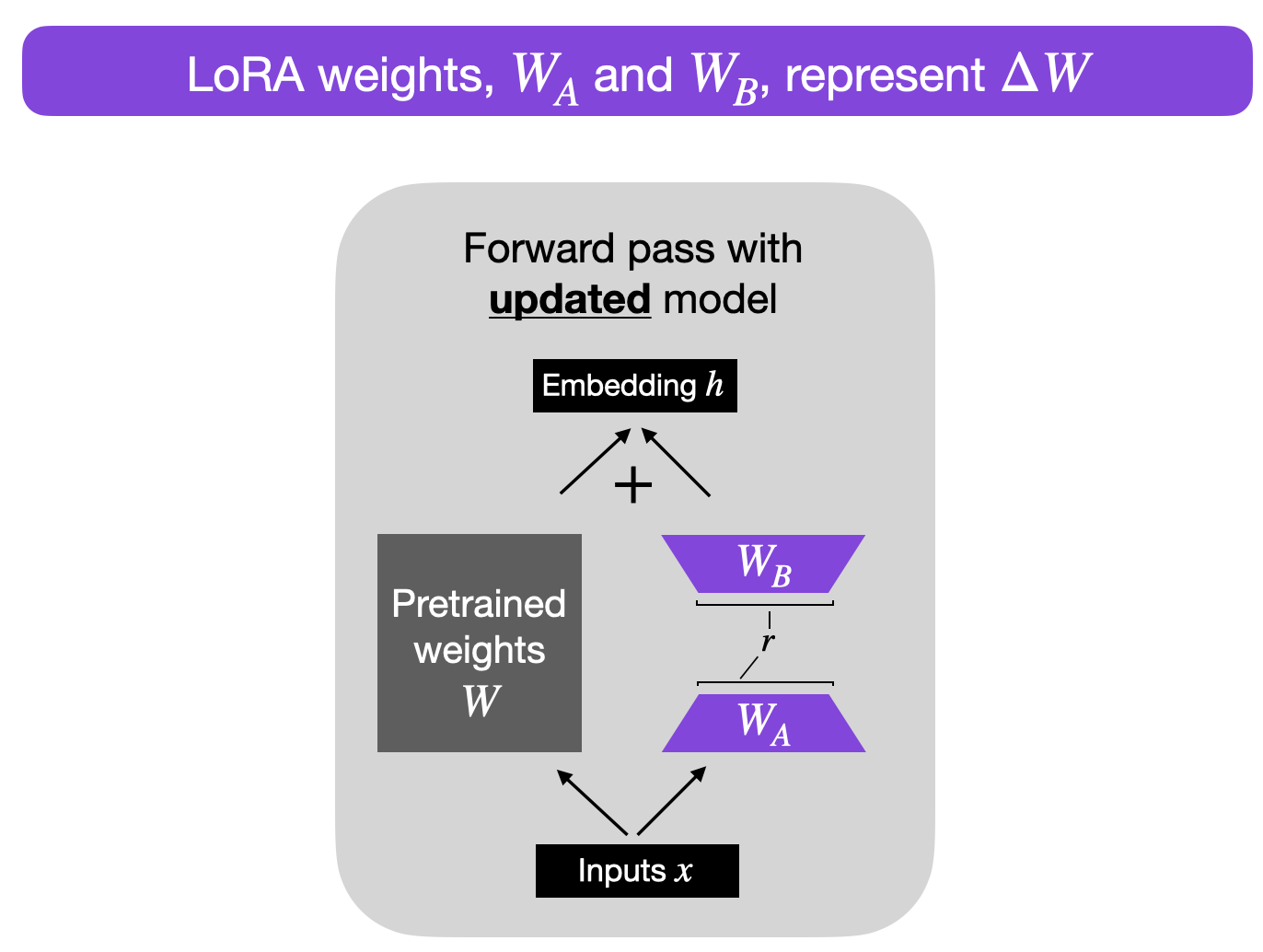
Training LLMs with a smaller amount of text can be challenging due to the model's need for large-scale data to capture the intricacies of language. However, with the LoRA technique and the Jaseci platform, it is possible to train LLMs even with limited text resources.
When working with a smaller dataset, it becomes crucial to maximize the data's utility and quality. Here are some strategies to consider:
Data Augmentation: Augmentation techniques can help increase the effective size of your dataset. By applying transformations such as synonym replacement, paraphrasing, or word shuffling, you can generate additional training examples. This approach helps introduce more diversity and variability into the data.
Pre-training: Leveraging pre-trained language models can be advantageous when working with limited text. By starting with a pre-trained LLM from platforms like Hugging Face, you can benefit from the model's already learned linguistic features. This pre-training phase acts as a foundation for further fine-tuning with your specific dataset.
Transfer Learning: Transfer learning allows you to take advantage of knowledge learned from one domain and apply it to another. You can start with a pre-trained LLM trained on a larger and more diverse dataset and then fine-tune it on your smaller dataset. This approach helps the model generalize better and capture specific patterns from your data.
Fine-tuning Strategies: LoRA's parameter-efficient methods are especially beneficial when working with limited data. These techniques focus on optimizing the architecture and training procedures to make the most out of the available text resources. By leveraging LoRA's attention mechanisms, representation techniques, and training optimizations, you can train LLMs with reduced computational requirements.
Active Learning: Active learning is a strategy where the model actively selects the most informative samples from the limited dataset for annotation. By iteratively labeling and training on the most valuable examples, the model can quickly improve its performance even with a small amount of data. This approach maximizes the efficiency of data utilization.
When training LLMs with limited text, it's important to set realistic expectations. The model's performance might not match that of models trained on massive datasets. However, with careful consideration of the available strategies and the utilization of LoRA's parameter-efficient techniques within the Jaseci platform, you can still achieve meaningful results and develop LLMs that exhibit useful language generation capabilities for your specific application.
The Jaseci platform provides a comprehensive framework for developing and deploying AI Applications. It offers a range of features that simplify the process, from setting up the model to training and generating. In this tutorial, we will focus on three core actions of the "llm" module within the JAC NLP package: Setup, Generate, and Train.